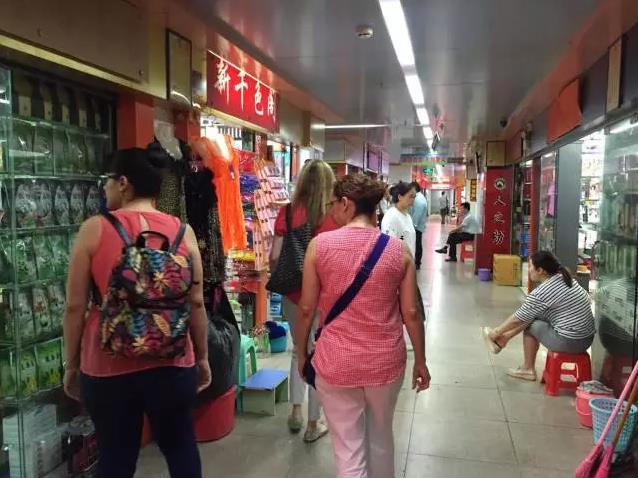
Hauling Logs, Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor-Coté, 1924
(National Gallery of Canada)
Thirty Acres (Trente Arpents)
by Ringuet (pseudonym of Philippe Panneton), 1938 translated by Felix and Dorothea WalterFall
The fall chapters of Trente Arpents start with he a praise of life on one’s thirty acres. It is a “un chemin paisible et long,” (a lengthy and peaceful road) despite various difficulties: storms, winter.
(And underneath, the soil forever faithful, eternally new and each year maternal.)[l]à-dessous, toujours, la terre constante, éternellement virginale et chaque année maternelle. (p. 149)
The land has a persistent face: “un visage (a face) persistant,” (p. 149) but as he praises the land’s persistence and fertility, Euchariste is confronted with a series of unfortunate events, some of which he has helped create…
Oguinase
Oguinase becomes a priest, but he does not live in a lovely parish and he works too hard. When Euchariste visits him, he is coughing and weak. He will soon die of tuberculosis. During Oguinase’s last visit home, he tells his sister Lucinda that she should not be sleeveless in the presence of an ordained priest. She feels offended and is not seen again.
The Conscription Crisis of 1917
Then comes conscription: World War I. Suddenly, these farmers remember pre-Revolutionary France: Christ and the King: “la France du Christ et du Roi.” (p. 158) They remember a somewhat revisionist Rebellion of 1837, called ’37. Would that they had a leader and were their own masters! The past is mythified.
Éphrem
Euchariste had hoped his son Éphrem would settle of his own thirty acres. There is money at the notary to buy “la terre des Picard,” the Picard’s farm, and Euchariste has even thought of a possible bride. There is no room for him on Euchariste’s thirty acres. The land cannot accommodate several sons. Yet Éphrem is not ready to become a farmer.
(It’s true, our land is good, but it isn’t very large.)C’est vrai que not’ terre elle est bonne, mais elle n’est pas ben grande! (p.163)
Éphrem eventually decides to leave for the United States. His uncle, Alphée Larivière (Walter Rivers), who visited during the summer, has found work for him in Lowell, Massachusetts. Later, Éphrem marries an Irish woman and moves to White Falls.
Phydime Raymond vs Euchariste Moisan
Oguinase dies, which saddens Euchariste immensely, and he then gets embroiled in an expensive legal battle with his neighbour Phydime Raymond. Decades ago, Euchariste sold a small piece of his thirty acres to Phydime, but Phydime is now taking more land that he bought.
Étienne: “le seul maître”
Matters do not improve. Having been burdened with legal fees Eucharist never thought would be astronomical, misfortune does not relent. One night Eucharist’s barn burns to the ground and he suspects that Phydime set fire to it. There are losses but the farm animals are safe. They had been removed immediately and a new barn is built but not according to Euchariste’s wishes. It is built according to Étienne’s standards. Étienne loves the land. Each year, it grows more and more into “a spouse and a lover:”
épouse et maîtresse, sa suzeraine [like a feudal lord] et sa servante, à lui Étienne Moisan. (p. 165)
Napoléon or Pitou: the arrangement
An arrangement is made. Étienne will run the farm with Napoléon, called Pitou. A new house will be built for Pitou and his family. All is arranged, except that Euchariste is in the way. It would now be convenient for him to live elsewhere. However, the notary leaves town taking with him Euchariste’s savings. He is dispossessed.
Winter
When the winter of his life begins, an impoverished Euchariste gives his land and his possessions to Étienne. In exchange, he will receive an allowance, a rente (a pension). But he is nevertheless again dispossessed, “land and beasts, gains and debts.” He is blinded by tradition: from father to son.
Il se ‘donna’, terre et bestiaux, avoir et dettes. (p. 219-20)
(He ‘gave’ himself, land, beasts, assets and debts.)
Euchariste has therefore lost his home. Étienne is now the only master: “seul maître.” (p. 220) He has already moved into the large house, which he hopes his father will soon leave. After all, Étienne is the new owner.
The Holiday in the United States: The “Exode”
Euchariste is therefore sent on a “holiday” to the United States to visit Éphrem who works in a factory and lives in White Falls. Euchariste is completely disoriented. Moreover, his daughter-in-law does not speak French, nor do his two grandchildren. Not once does his daughter-in-law express pleasure at his being in their household. In fact, Sunday mass becomes Euchariste’s only respite.
Sundays: the only day
Sunday is the only day Euchariste meets a few persons who do not feel at home in the United States. It has been a long and disappointing holiday, all the more since Étienne has not been sending the monthly allowance, la rente (the pension), he had promised he would give his father in return for ownership of Euchariste’s lost thirty acres.
Going home has therefore become difficult. In fact, Euchariste has no home and, suddenly, the market crashes and he is “needed” in the United States. The factory where Éphrem has been working for six years is letting people go or making them work on a part-time basis.
The Great Depression: Euchariste returns to work
Therefore, an older and sadder Euchariste wants to work again, possibly for a farmer. Éphrem finds a job for his father, that of night watch in a garage. But, Euchariste hesitates to accept this position, not because he will not work on a farm, but for fear of falling asleep for a moment and being remiss in his duties. Times have changed!
(What terrified him at first, was fear that he would fall asleep and fail for a moment to be vigilant, which was his duty [devoir]).Ce qui le terrifiait au début, c’était la crainte de s’endormir, de manquer un instant à son devoir de surveillance. (p. 268)
He earns fifteen dollars a week, but Éphrem takes ten of the fifteen dollars. Moreover, Étienne also wants money. It is as though there had been no arrangement between Étienne and Pitou. Euchariste is therefore needed not only in the US but also in Canada. His daughter Marie-Louise is sick. She is dying of tuberculosis and needs medical care, which is expensive. She soon dies.
* * *
At the end of the novel, Euchariste is depicted as a very frail old man huddling near a little stove in the garage where he works.
Yet, although it is sad, the end is also poetical. Ringuet takes us away from the plight of one man to the plight and joy of mankind, or from the particular to the general. He writes that every year spring returns and that, every year, the land is generous. The land is always the same, toujours la même, not to the same men, men pass, but to different men:
…à des hommes différents… …une terre toujours la même. Suggested reading: The Canadian Encyclopedia Ringuet (Athabaska University)—ooo—
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky (7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) Andante Cantabile Yo-Yo Ma, Cello
After the Breakup, Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor-Coté, 1914 (National Gallery of Canada)
Filed under: Art, Canadian History, French-Canadian Literature, Quebec, Regionalism Tagged: Dr Philippe Panneton, Euchariste Moisan, Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor Coté, Regionalism, Ringuet, the Great Depression, Thirty Acres, Trente arpents, United States